Understanding Blocks in Scout Workflows
Blocks are the foundational elements of any workflow in the Scout platform, acting as modular units that carry out specific tasks within a process. Each workflow begins with an input block, which receives initial data or a trigger, setting the stage for the series of actions that follow. The versatility of blocks allows users to construct complex logical flows and achieve a wide range of automation objectives.
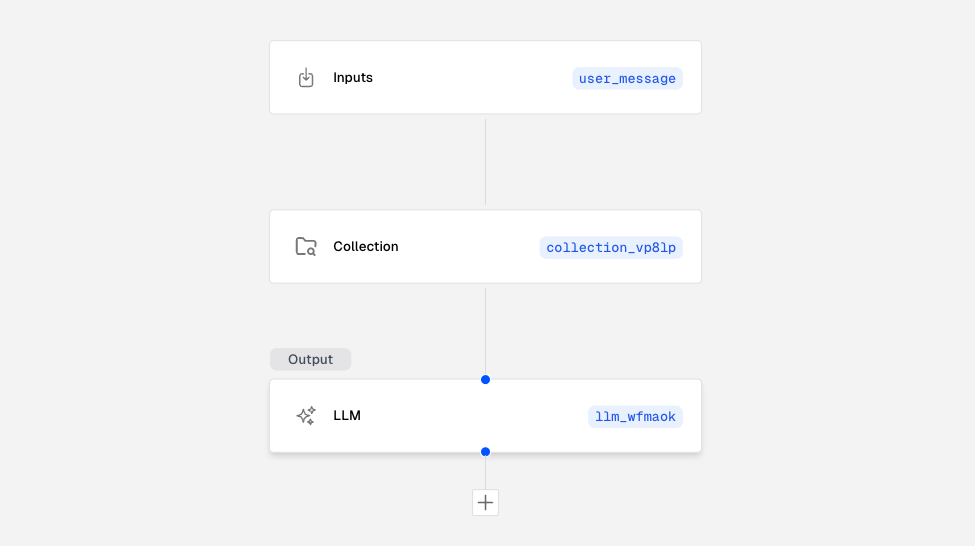
Blocks are designed to be both composable and customizable, enabling the creation of intricate processes by linking various types of blocks in a sequence. Each block performs a unique function, such as querying a database, sending an HTTP request, or processing text with an LLM. This modularity ensures that workflows can be tailored to specific use cases, whether for data processing, API integration, or automated reporting.